Next Post
Augmented video application
Explore how augmented video applications allow developers to overlay geospatial information on video feeds, enhancing the user's understanding of the environment.
View PostIn this article, terrain warning in 2D and 3D using Carmenta Engine is described. Terrain warning is an analysis used to visualize vertical distance to the ground for an area around an aircraft. The article explains how map configurations for terrain warning can be created using TerrainWarningOverlay and the TerrainWarningOperator.
All examples in this article are from the samples terrain_warning_2d.px and terrain_warning_3d.px provided with the SDK.
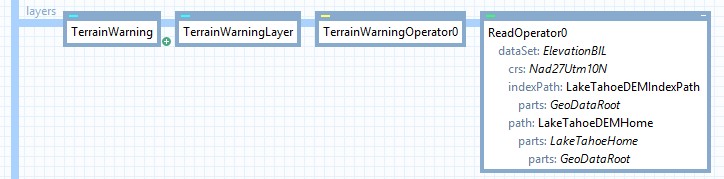
For terrain warning in 2D, a TerrainWarningOverlay and a TerrainWarningOperator is required.
The TerrainWarningOverlay controls the visualization of the terrain warning, while the TerrainWarningOperator provides the ground elevation data to the TerrainWarningOverlay.
The TerrainWarningOverlay is an Overlay used to configure the visualization of the terrain warning. A TerrainWarningOverlay is created and added to the TerrainWarningOverlay property of the View.
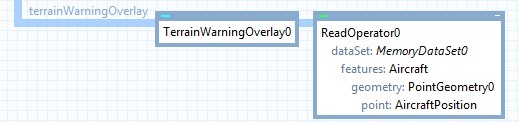
The position of the aircraft used for the terrain warning can be set in two ways.
The Position property can be used to set the position of the aircraft using a Point. Alternatively, the Input property can be used to set an operator providing a point feature corresponding to the aircrafts position. Having an operator providing the aircraft feature allows the aircraft feature to be reused in other places in the map configuration, for example for visualization of the aircraft feature. If both properties are set, the feature from the Input property will be used.
The example above uses a ReadOperator to read the aircraft feature from a MemoryDataSet, which is also used for visualization of the aircraft.
The MaxDistance property controls the max distance in meters from the aircrafts position where the terrain warning is displayed.
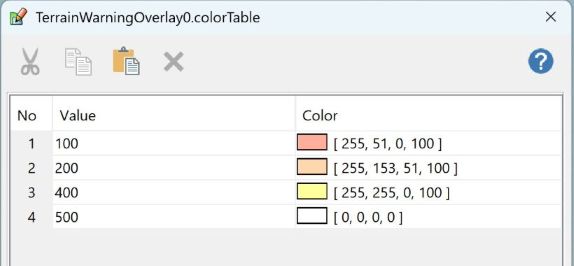
The ColorTable property determines the coloring based on the vertical distance between the ground and the aircraft. The color table below shows a configuration where a distance of less than 100 m is visualized with a red color, a distance between 100 m and 200 m with an orange color, and so on.
When setting up terrain warning in 2D, a TerrainWarningOperator is needed. The TerrainWarningOperator is used to tag the ground elevation data to enable the TerrainWarningOverlay to use it in the analysis. The TerrainWarningOperator is added as a layer on the View, in this case using an OrdinaryLayer and a TileLayer. The Input property on the TerrainWarningOperator is set to an operator reading ground elevation data.
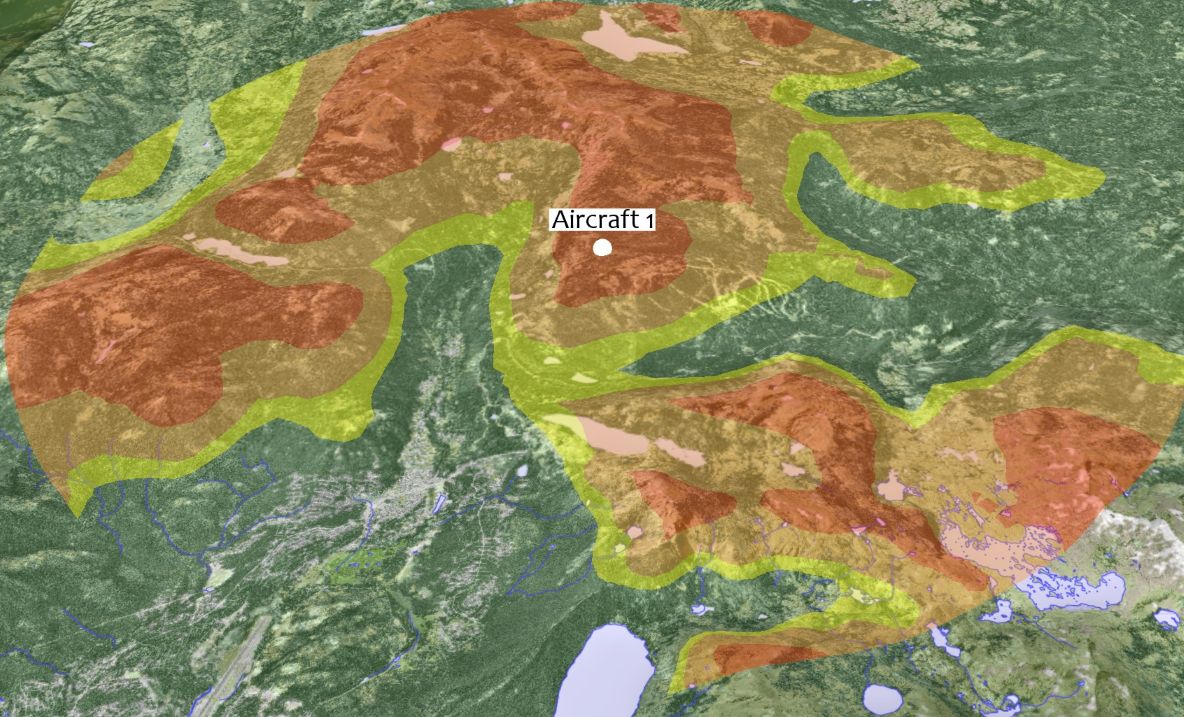
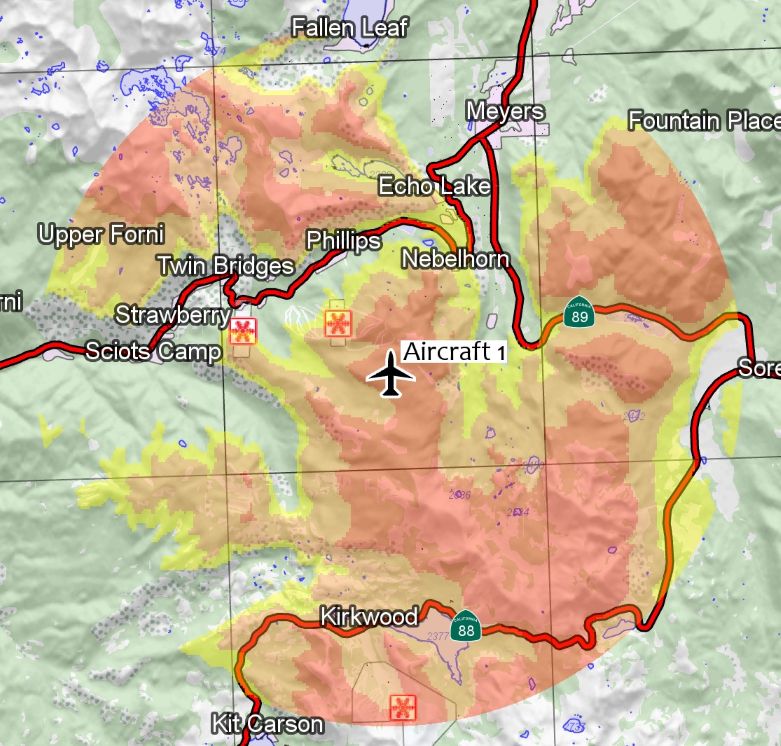
The picture below shows terrain warning in 2D.
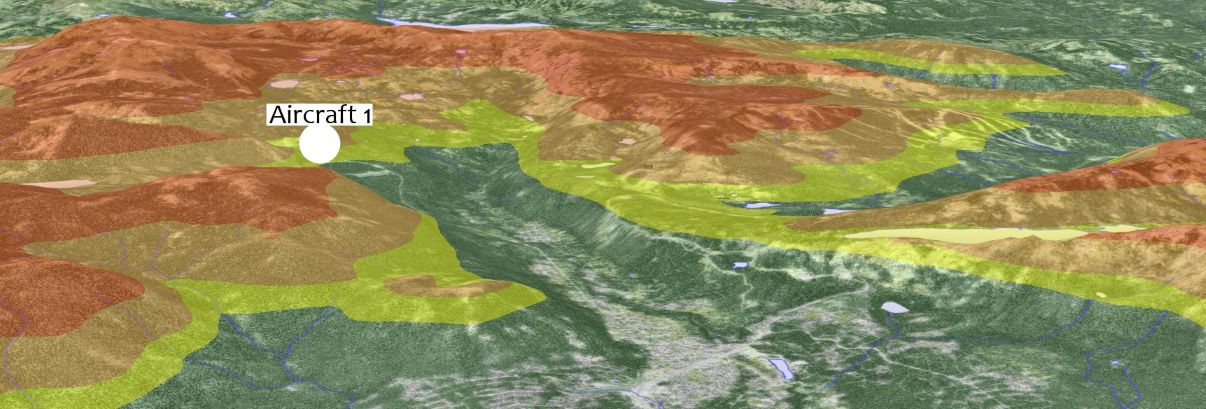
To set up terrain warning in 3D, a TerrainWarningOverlay is configured and added to the view in the same way as for 2D. However, a TerrainWarningOperator is not required. The reason is that the View is of type GlobeView for 3D, and therefore already has access to ground elevation data via the ElevationInput property. However, a TerrainWarningOperator can be used if we want to use additional input for the terrain warning, for example buildings. In such case, it is configured in the same way as in 2D.
The picture below shows terrain warning in 3D.
This article has described how terrain warning in 2D and 3D can be set up using Carmenta Engine. We have introduced the TerrainWarningOverlay, which controls the visualization of the terrain warning, and the TerrainWarningOperator, which provides ground elevation data in 2D.

Explore how augmented video applications allow developers to overlay geospatial information on video feeds, enhancing the user's understanding of the environment.
View Post
In this guide, we explore the process of building a basic application using Android Studio and Kotlin, specifically targeting Android 9 (API 28, Pie).
View Post