Use Cases and Applications
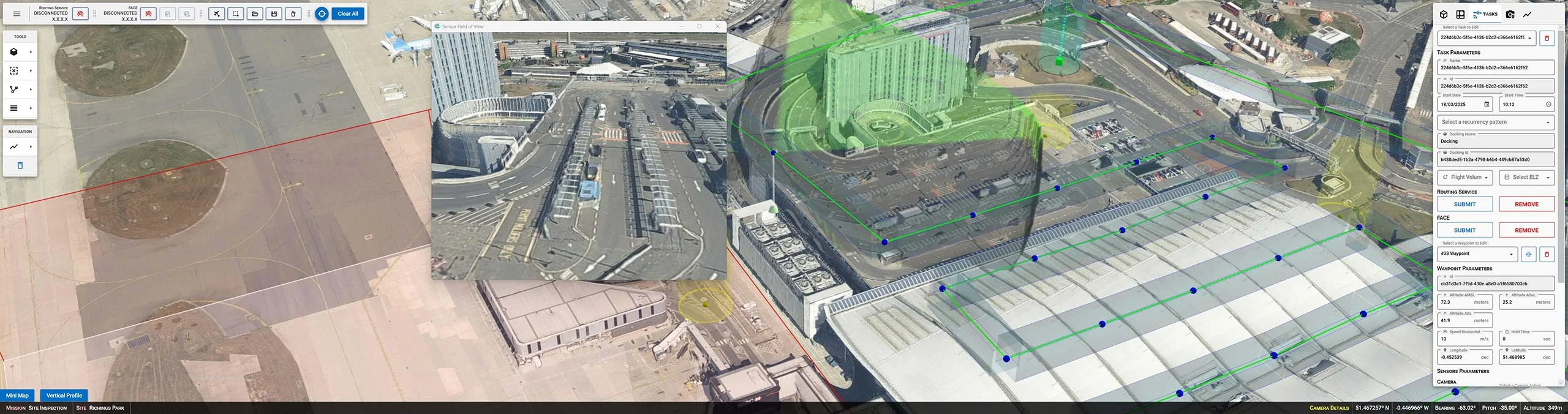
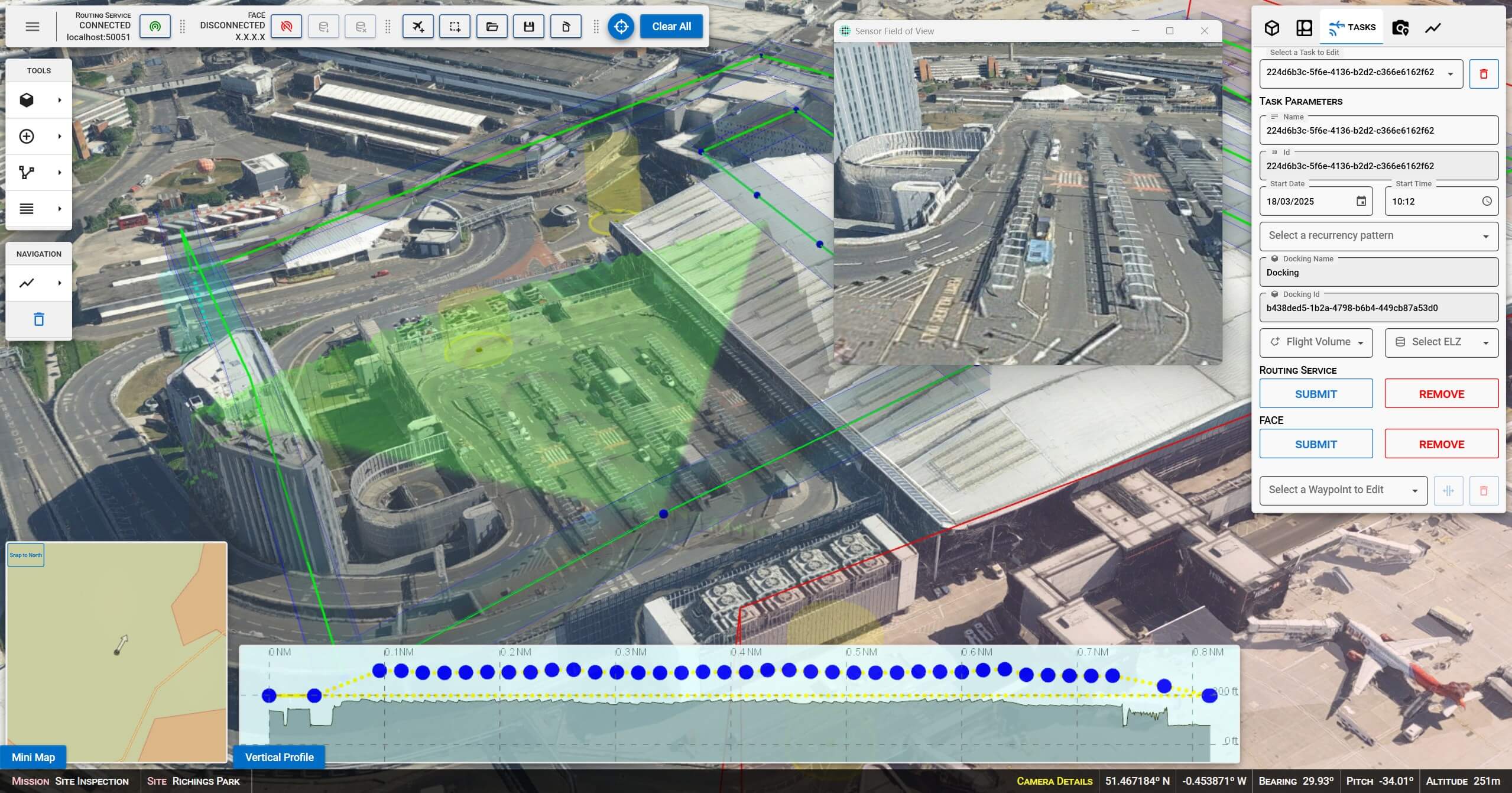
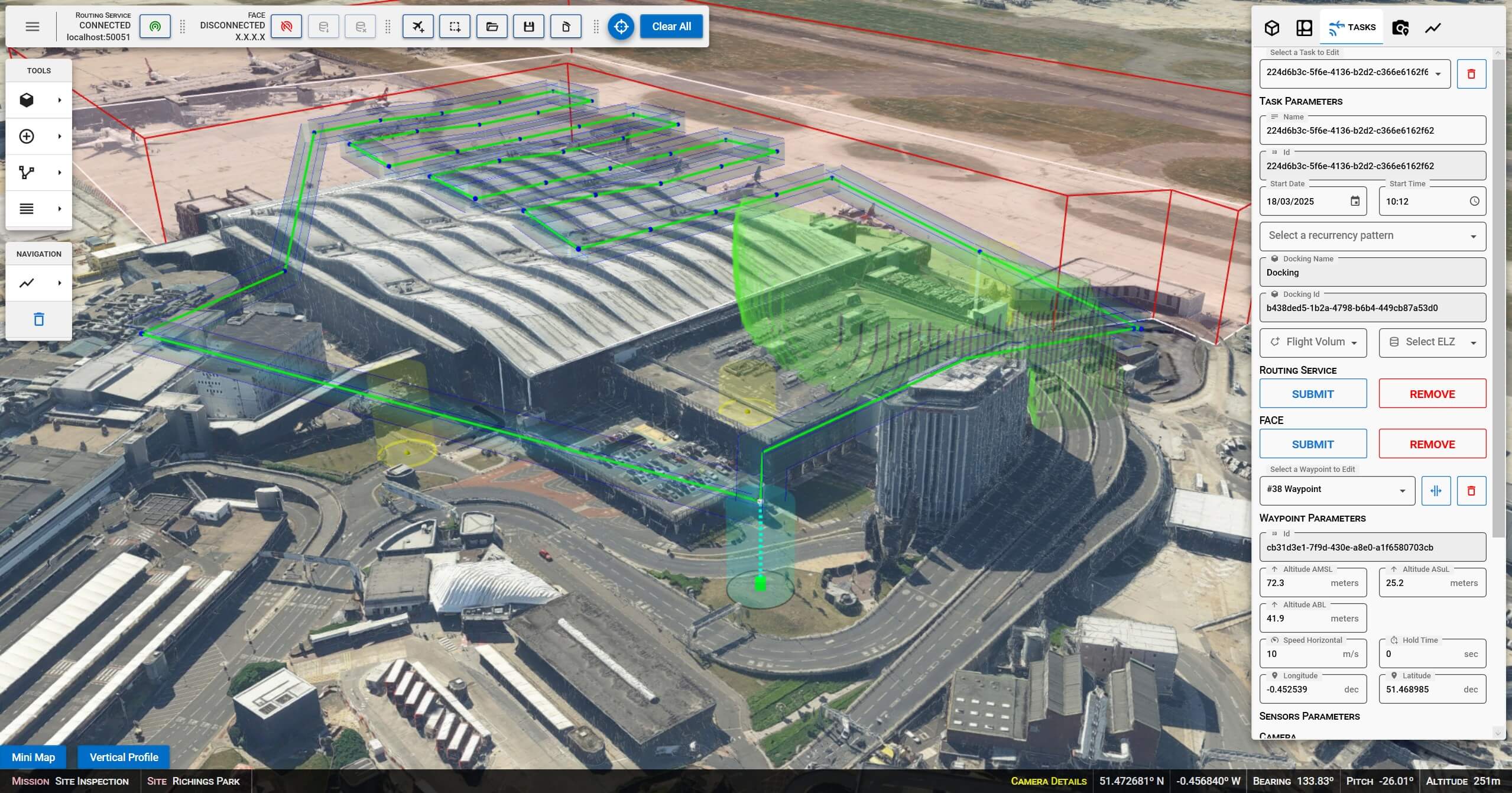
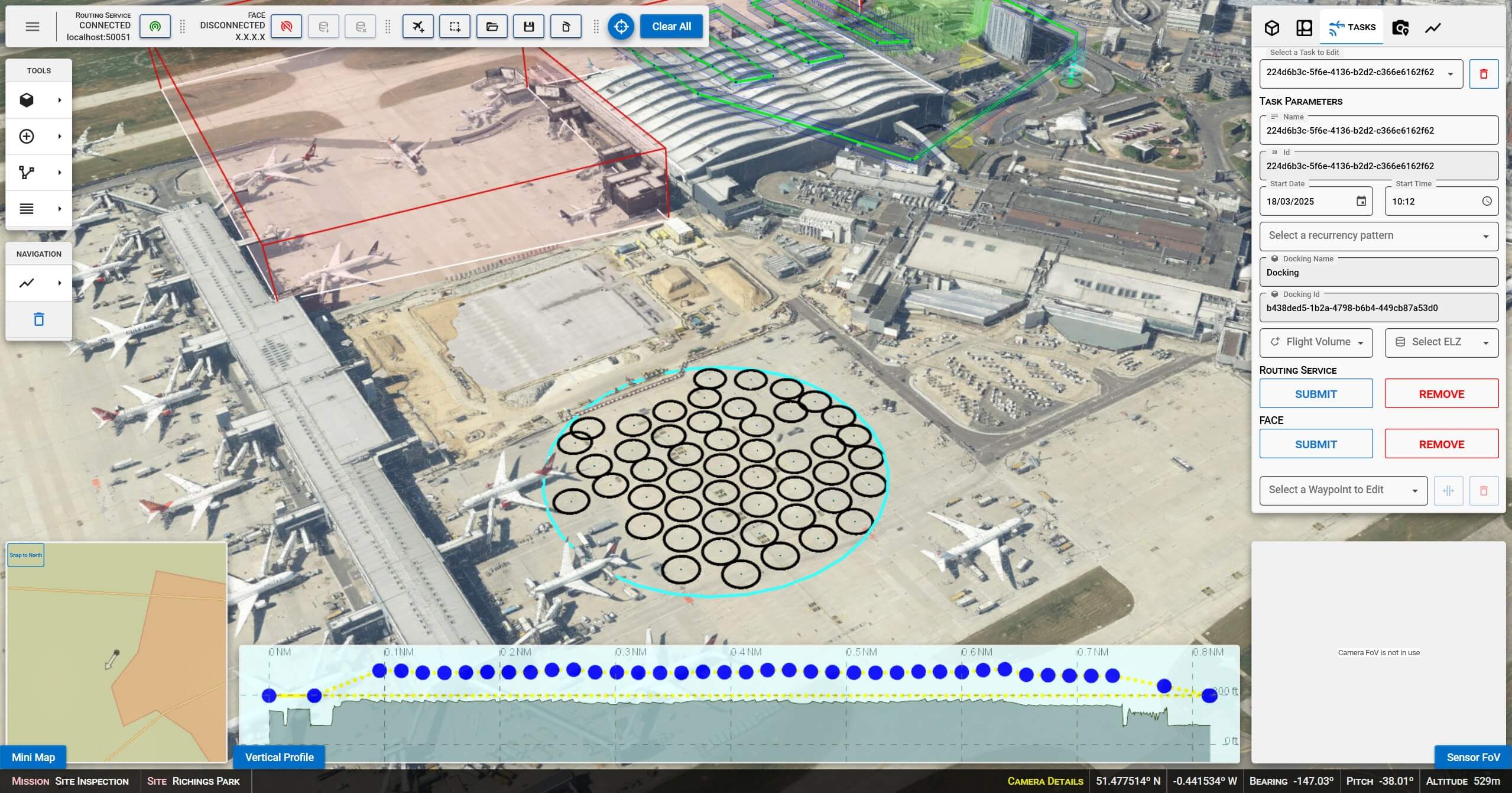
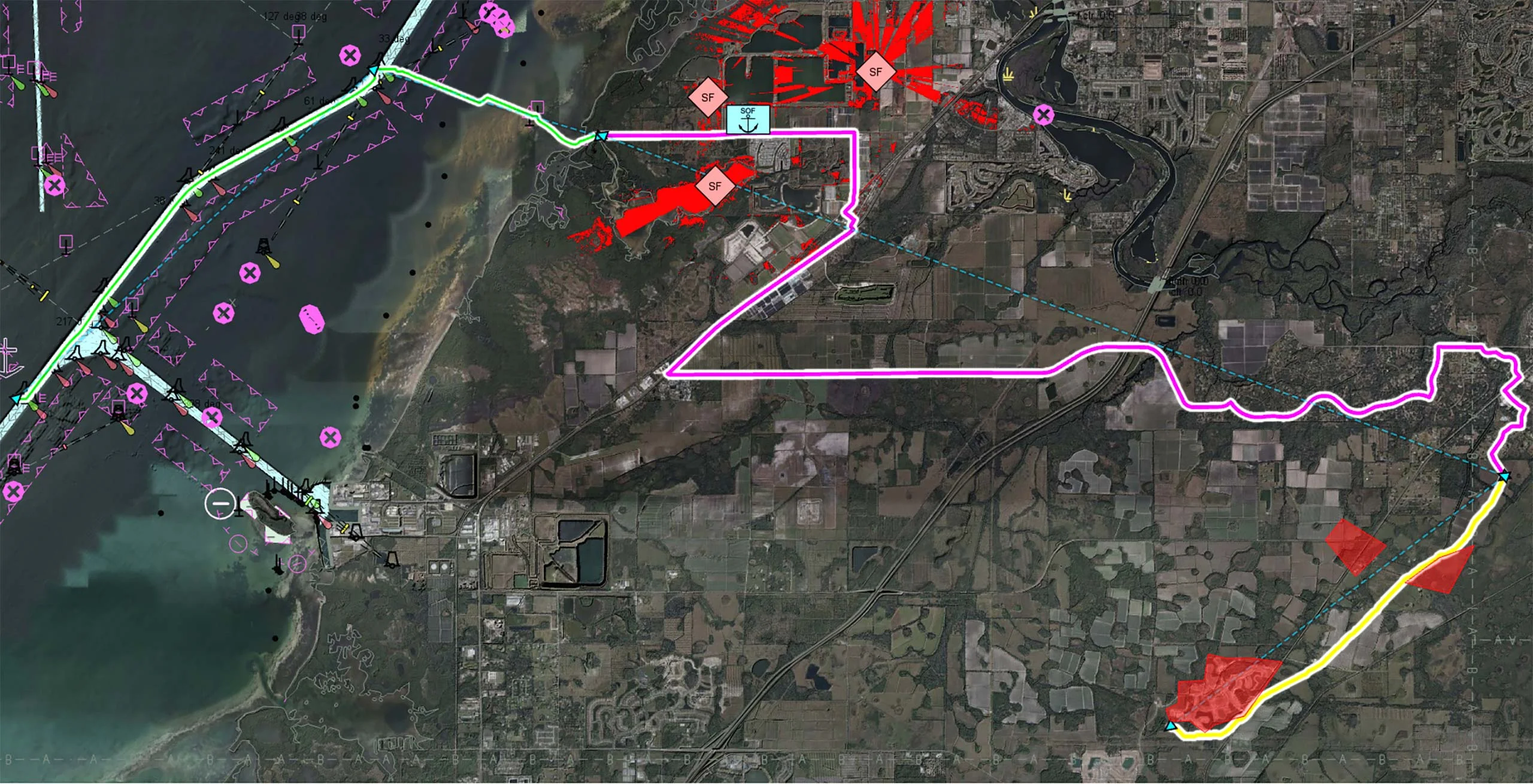
The project explored various use cases for autonomous drone operations, including perimeter surveillance, infrastructure inspection, and incident response. Capabilities developed by Carmenta in the project includes a 3D Graphical User Interface to plan UAS Missions and a set of backend services. The backend services were created to process flight plans, generate optimised routes for fence inspection, roof inspection, building inspection, apply route and obstacle deconfliction, and recommend landing zones for emergency procedures.
To generate optimal routes, obstacles such as buildings, restriction areas, overlapping UAS flight corridors, and sensor coverage need to be considered. If conditions for a route change, the route has to be regenerated and adapted in real-time.