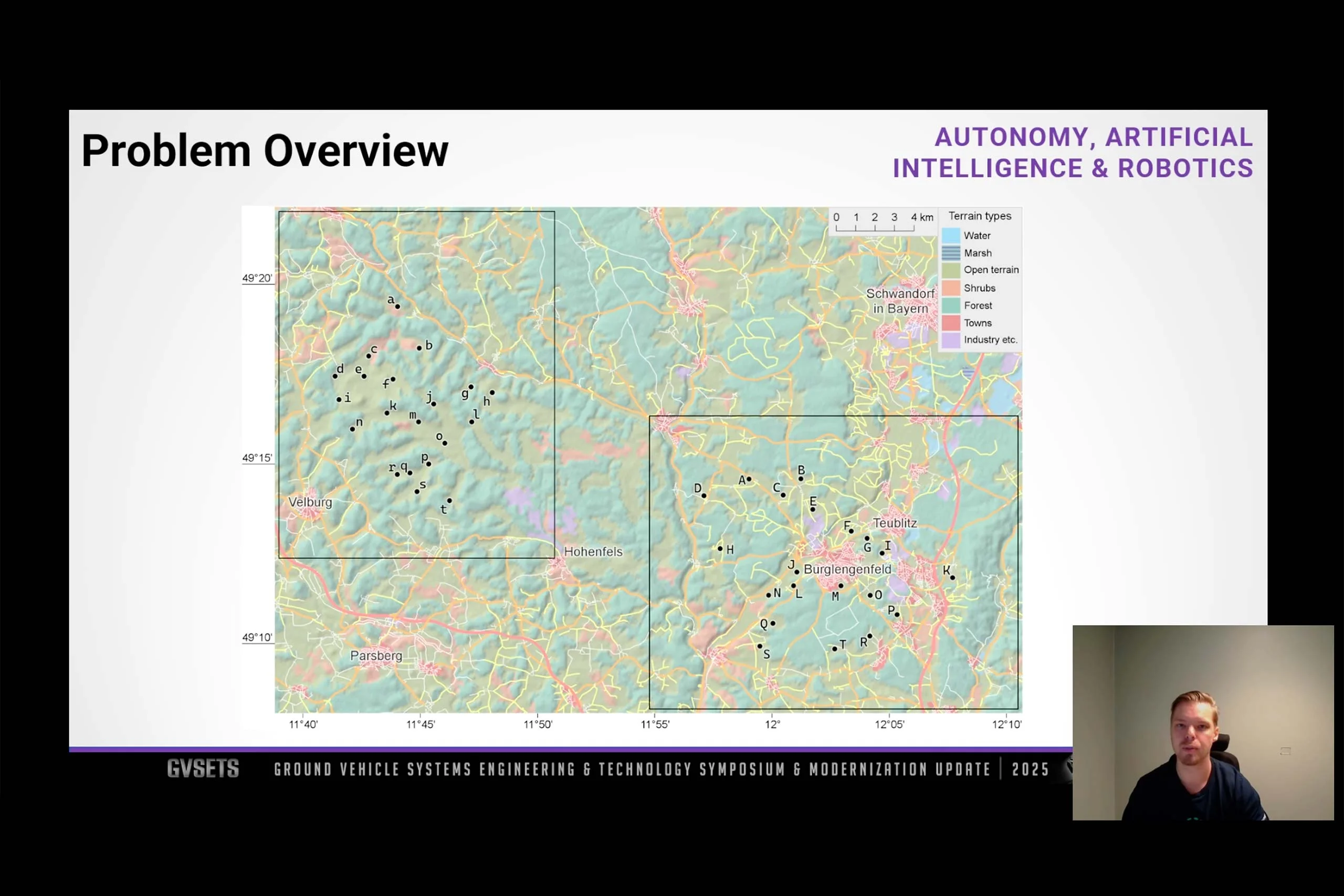
Enhancing Performance with the Shortest Path Tree Problem
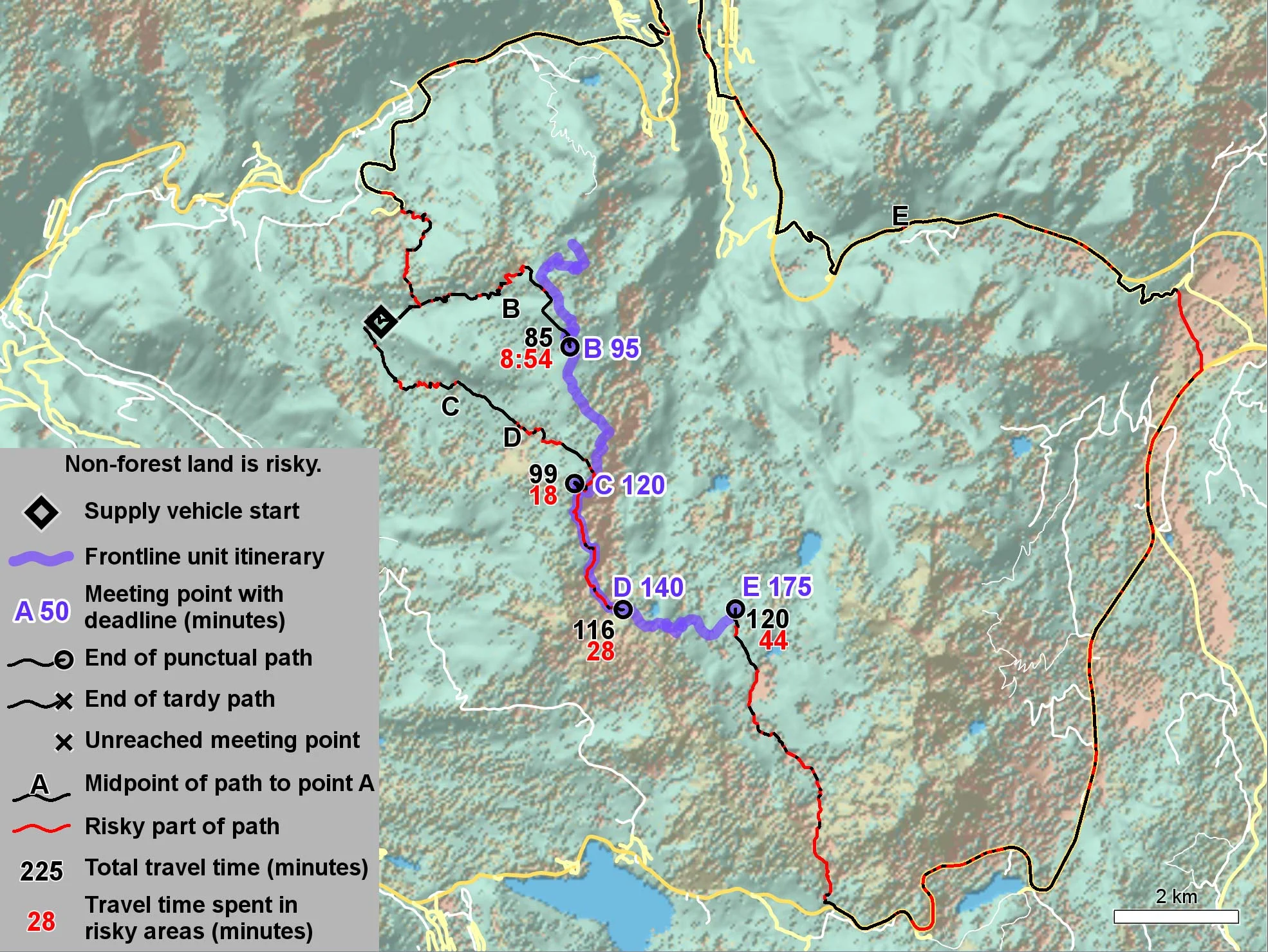
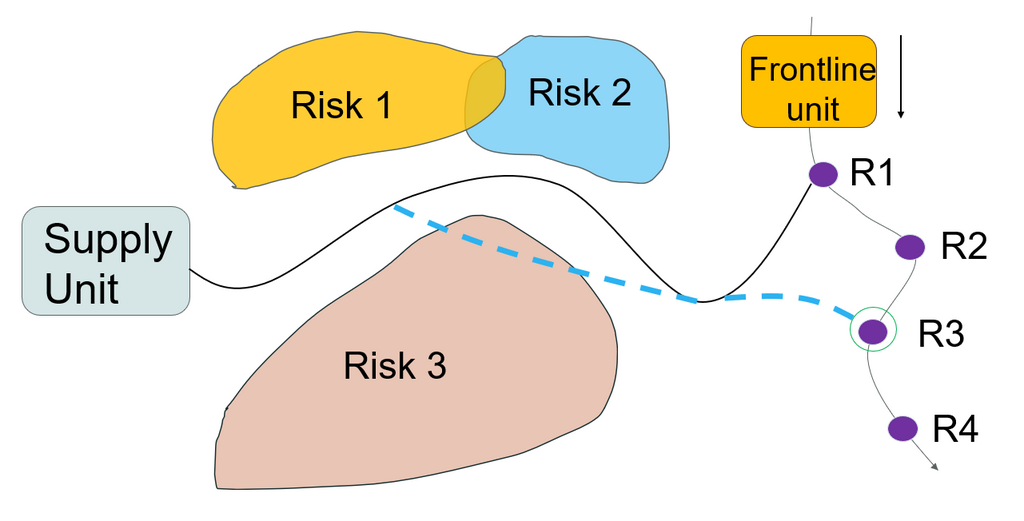
To speed up the evaluation among the many possible rendezvous points, the shortest path tree problem is employed, generating all possible routes from the supply vehicle’s current location within a defined a search area. If large enough, this area covers all rendezvous points from which routes can later be reconstructed again, dramatically increasing performance.
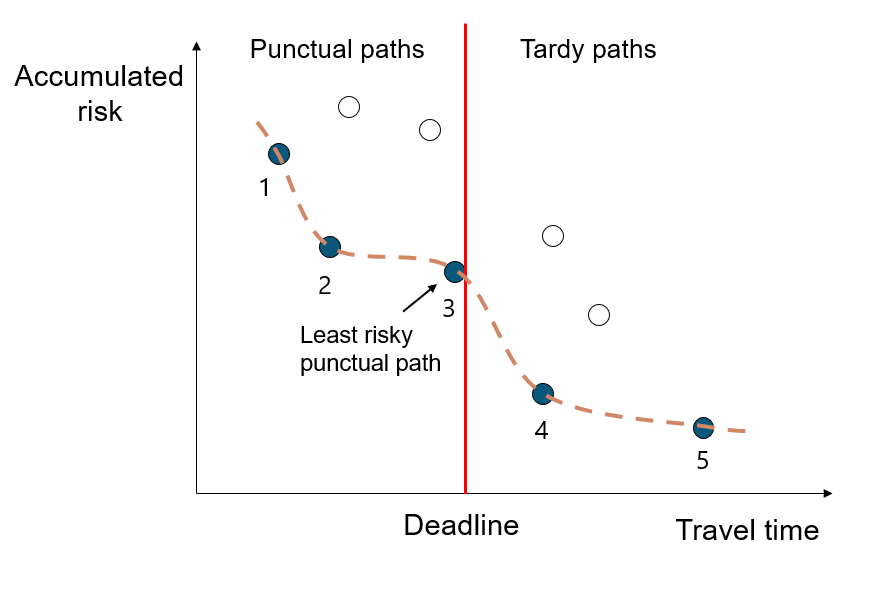
Bisection Iteration for Optimal Path Identification
Using bisection iteration, the AIPP algorithm successfully identifies the least risky route to the optimal link-up point that also meets the rendezvous deadline. Alternatively, the AIPP algorithm can produce a set number of alternatives, each presented with an estimated time of arrival and threat exposure time, outlining challenges along the route.
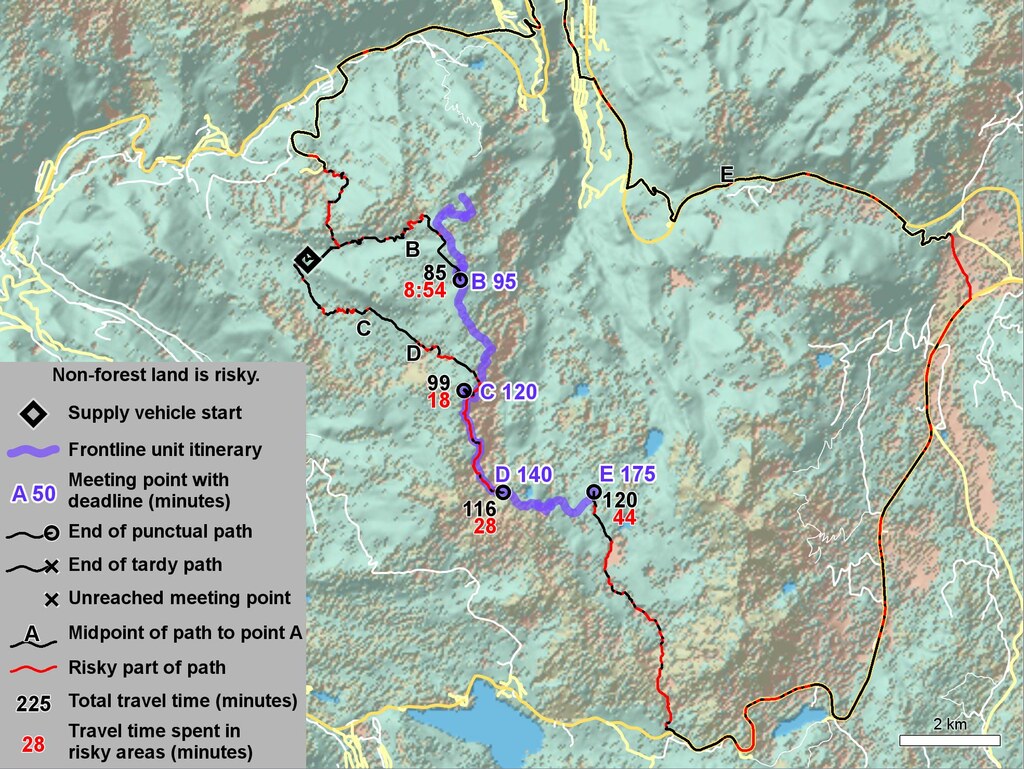
Figure: AIPP results using safety factor s = 1/2, iteration three.